Energy pathways during the workout
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the chemical energetic unit that human body uses for energy and transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. The human body is capable of producing ATP using three different pathways.
- Aerobic pathway
- Anaerobic lactic pathway
- Anaerobic alactic pathway
The energy for those pathways comes from the food that mainly consist of protein, carbohydrates and lipids with 1 g of proteins has the energy approximately 4.1 kcal, 1 g of carbohydrates 4.1 kcal and 1 g of lipids 9.0 kcal. Production of ATP using different energy pathways is time and intensity related. Exercising at very high intensity is possible only for a very short time period, while in contrast exercising lower intensities can be sutained for very long periods.
If working at almost maximal intensity for the following time periods, the energy from different pathways is limited and can be sustained from couple of seconds until several hours. It is also important to consider that there is almost no situation when the energy to produce ATP comes from one energy pathway only, all three pathways are always included. However, at maximal intensities 95-99% of energy comes anaerobic alactic pathways while at marathon run 99% from aerobic pathway.
Table 1. Different lengths of exercises at nearly maximal intensity and the corresponding energy sources.
| Duration fo exercise |
Main energy pathway |
Energy supplied by |
| 1 to 5 secods |
Anaerobic alactic |
Muscle ATP |
| 5 to 10 seconds |
Anaerobic alactic |
ATP + creatinephoshpate (CP) |
| 10 to 45 seconds |
Anaerobic lactic |
Muscle glycogen + CP |
| 45 to 120 seconds |
Anaerobic lactic |
Muscl glycogen |
| 2 minutes to 6 minutes |
Aerobic, anaerobic lactic |
Muscle glycogen |
| 6 minutes to 30 minutes |
Aerobic |
Glycogen + lipids |
| 30 minutes to 1-2 hours |
Aerobic |
Lipids |
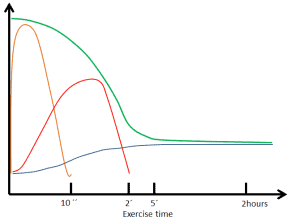
All three energy systems contribute to energy production from the start of the exercise but the time their contribution is different . For example, aerobic energy system reaches it maximum energy production after about 1.5 to 2 miuntes. So far the rest of energy must be covered by anaerobic pathways.
Figure 1. The contribution of energy systems during physical workout. (Modified from Davis et al. 2000).
Table 2. Different contributions of the energy sytems during various disciplines
References:
Davis B et al. (2000). The interrelationship of the energy system and their threshold points. In: Physical Education and the Study of Sport. Hartcourt, UK.